ASTM A36 vs JIS SS400: Structural Steel Differences and Equivalency
414Compare ASTM A36 vs SS400 structural steel. Understand yield strength differences, thickness effects, and whether SS400 can replace A36 in engineering projects.
View detailsSearch the whole station

Choosing the right steel for appliance manufacturing directly affects surface quality, forming efficiency, cost control, and long-term product performance. Among all flat-rolled steel products, cold rolled steel and hot rolled steel are the two most commonly compared options for home appliances.
This guide focuses specifically on cold rolled vs hot rolled steel for appliances, explaining how each material performs in appliance manufacturing and which is more suitable for different appliance components.
Cold rolled steel is produced by further processing hot rolled steel at room temperature. After hot rolling, the steel is pickled (to remove scale), then rolled in a cold reduction mill, which compresses the steel into precise dimensions and improves its surface quality.
For appliance manufacturing, this material is commonly referred to as appliance cold rolled steel.
These properties make cold rolled steel for appliances especially suitable for parts that require a clean appearance, accurate fit, and stable forming behavior during stamping or bending.
Typical supply forms include:
For specifications and pricing of cold-rolled steel plates for appliances, visit our product page: Cold-Rolled Steel Plate for Home Appliances.
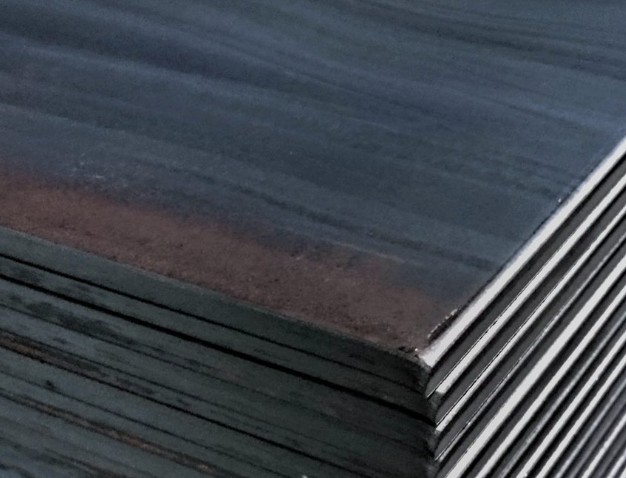

Hot rolled steel is produced at high temperatures, typically above the recrystallization point. This allows the steel to be rolled easily into thicker sections, but surface oxidation and dimensional variation occur during cooling.
In appliance manufacturing, hot rolled steel for appliances is generally limited to non-visible or structural components.
Typical characteristics include:
Because of the surface condition, hot rolled steel usually requires additional processing if appearance or coating quality is important. As a result, it is less commonly used for external appliance panels.

The difference between hot rolled and cold rolled steel becomes especially important when applied to appliance production rather than general steel use.
| Feature | Cold Rolled Steel | Hot Rolled Steel |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Temperature | Room temperature (after hot rolling) | >1,700°F (hot rolled directly from billet) |
| Surface Finish | Smooth, uniform, matte or shiny | Scaled, rough surface |
| Dimensional Precision | High tolerance | Lower tolerance |
| Strength | Higher (after work hardening) | Lower |
| Formability | Excellent (after annealing) | Fair, better for bending without cracking |
| Applications | Appliances, furniture, automotive components | Construction beams, welding structures |
| Thickness Tolerance | Tight control, uniform across the coil | Variable across sheet width |
| Cost | Higher due to processing | Lower, less processing |
From a manufacturing perspective, cold rolled steel offers better consistency and surface quality, while hot rolled steel is mainly selected for cost-sensitive internal parts.
Looking for other types of cold rolled plate? Explore our full product range here: Cold Rolled Steel Plate – Full Series.
In most appliance applications, cold rolled steel is stronger than hot rolled steel.
The increased strength comes from work hardening during the cold rolling process.
However, the actual strength difference depends on:
For appliance components that require higher rigidity without increasing thickness—such as brackets, drawer supports, or reinforcement parts—cold rolled steel provides a clear advantage.
Instead of comparing steel types in general terms, appliance manufacturers typically select materials based on the function of each component.
| Appliance Component | Recommended Steel | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| Refrigerator outer panels | Cold rolled steel | Surface quality and coating performance |
| Washing machine housings | Cold rolled steel | Formability and dimensional accuracy |
| Microwave oven frames | Cold rolled steel | Precision and appearance |
| Internal support brackets | Hot rolled steel | Cost efficiency |
| Structural base plates | Hot rolled steel | Thickness and load support |
This decision-based approach explains why cold rolled steel dominates visible appliance parts, while hot rolled steel is used selectively for internal structures.

Modern appliance manufacturing relies heavily on automated stamping, forming, welding, and coating processes.
Cold rolled steel aligns well with these requirements because it offers:
For these reasons, appliance cold rolled steel has become the standard material for most appliance OEMs.
Let’s address a few final questions that buyers often search:
A: The difference lies in processing temperature and resulting properties. Cold rolled steel offers better surface finish and tighter tolerances.
In the appliance industry, hot rolled steel is mainly used for internal or non-visible components, such as support frames, base plates, and welded structural parts where surface appearance is not critical.
A: Cold rolled steel is widely used for appliance panels, housings, cabinets, and precision-formed parts. Its smooth surface and consistent thickness make it suitable for painting, coating, and automated forming processes.
A: “Appliance cold rolled steel” refers to cold rolled steel specifically used for home appliance production. It is valued for its clean surface quality, precise tolerances, and stable forming performance, which are essential for appliance exteriors and structural components.
A: Yes. Hot rolled steel can be used in appliances, but it is generally limited to internal structures. For external panels or visible parts, cold rolled steel is usually preferred due to its superior surface finish.
A: Check our Cold-Rolled Steel Plate for Home Appliances product page for specifications and pricing.
For appliance manufacturing, material selection depends on component function rather than a single “better” option.
In most cases, cold rolled steel is the preferred material for appliances because it meets appearance, forming, and production efficiency requirements.
For specifications and supply options related to cold rolled steel for appliances, you can refer to our appliance-grade cold rolled steel product range.
Looking for cold-rolled steel sheets for appliance manufacturing or need advice on the right build? Contact us today and our team will help you get the ideal solution.
Compare ASTM A36 vs SS400 structural steel. Understand yield strength differences, thickness effects, and whether SS400 can replace A36 in engineering projects.
View detailsGet a free H beam size chart, dimensions, and weight table for construction projects under global standards. CJM Steel supplies H beams - request a quote today.
View detailsCompare S355JR, S355J2, and S355NL steel grades under EN 10025. See yield strength, toughness, equivalents, and applications for construction & offshore use.
View detailsCarbon steel pipe is strong, durable, and widely used for transporting fluids and gases in various industries.
View details
HelloPlease log in