Which Is Better for Appliances: Cold Rolled or Hot Rolled Steel?
1066Compare cold rolled vs hot rolled steel for appliances. Learn which steel suits appliance panels, frames & manufacturing needs based on strength and cost.
View detailsSearch the whole station
Galvanized steel sheets are a core material in global infrastructure and manufacturing, valued for their exceptional corrosion resistance, structural strength, and versatility. Their widespread adoption spans civil construction, transportation, agriculture, energy, and white goods industries.
This article presents a comprehensive analysis of galvanized steel sheet products—covering production methods, international standards, mechanical properties, typical use cases, and considerations for industrial sourcing, with a particular focus on galvanized steel mechanical properties, zinc coating specifications, and international grade selection for industrial applications.
Quick Navigation
Galvanized steel is produced by coating carbon steel with a layer of zinc, typically through hot-dip galvanizing. This process significantly improves the steel’s resistance to corrosion and atmospheric oxidation. Zinc coating not only serves as a barrier against environmental exposure but also offers cathodic protection, whereby the zinc sacrifices itself to protect the underlying steel if the coating is damaged.
The longevity of galvanized steel sheets is one of their key advantages, with lifespans exceeding 20–50 years depending on coating thickness and environmental exposure.
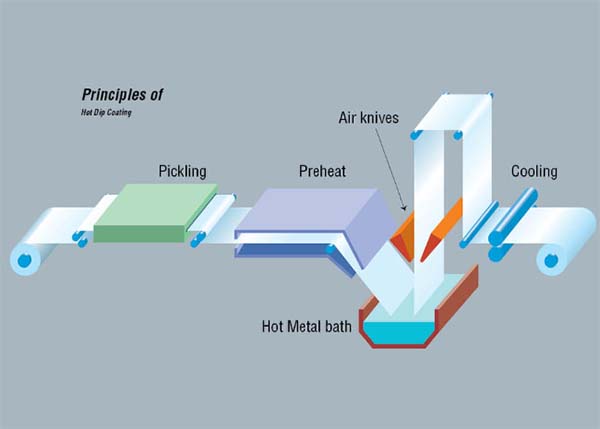
In this process, steel sheets or coils are immersed in molten zinc at approximately 450°C, forming a metallurgical bond between the zinc and the base metal. The resulting zinc-iron alloy layers provide excellent adhesion and wear resistance, making this method ideal for structural and outdoor applications.
This technique uses electrical current to deposit a thin layer of zinc onto the steel surface. It results in more uniform and aesthetically pleasing coatings, though with less corrosion resistance compared to HDG. Electro-galvanized steel is often used in electronics and automotive inner panels.
Most galvanized sheet products are produced using continuous lines that combine rolling, annealing, cleaning, and galvanizing in a single integrated process. This ensures consistency in coating thickness, surface finish, and dimensional control.
Galvanized steel is typically processed and supplied in the following formats:
| Form | Thickness Range (mm) | Width Range (mm) | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Galvanized Steel Sheet | 0.30 – 3.00 | 600 – 1500 | Flat panels used in construction and enclosures |
| Galvanized Steel Coil | 0.30 – 3.00 | 600 – 1500 | Coiled form, suitable for slitting or roll forming |
| Galvanized Steel Plate | 3.00 – 25.00 | 1000 – 2500 | Heavy-duty material for structural applications |
Sheets are favored in roofing, siding, and interior fabrication, while coils allow for easy transport and processing. Plates are used in structural members, bridge decks, and machinery supports.
Several global standards govern the quality and performance of galvanized steel. Commonly referenced specifications include:
| Standard | Country/Region | Common Grades | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|
| ASTM A653 | USA | CS Type A/B, SS Grade 33–80 | General & structural steel work |
| JIS G3302 | Japan | SGCC, SGCD, SGCE | Deep drawing, forming, bending |
| EN 10346 | Europe | DX51D+Z, S220GD–S550GD | Structural steel, roofing systems |
| IS 277 | India | Designations by coating mass | Utility and general fabrication |
Grades differ in mechanical strength, ductility, and coating weight. Coating designations such as Z100 or Z275 refer to the total zinc mass per square meter.
The performance of galvanized steel is directly influenced by the weight and consistency of its zinc coating. Typical coating levels include:
| Coating Grade | Zinc Mass (g/m²) | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Z60 | 60 | Indoor structures, short-life components |
| Z120 | 120 | Automotive, residential roofing |
| Z275 | 275 | High-corrosion zones, coastal buildings |
The galvanized steel sheet price is influenced heavily by the coating weight and base steel grade. Thicker coatings provide better durability but may affect weldability and forming properties.
The mechanical performance of galvanized steel sheets is determined primarily by the base steel grade, while the zinc coating provides corrosion protection without significantly changing the structural strength. For engineering design, fabrication, and material selection, key galvanized steel mechanical properties—including yield strength, tensile strength, elongation, and hardness—are the most frequently evaluated.
Below are typical values for widely used grades:
| Grade | Yield Strength (MPa) | Tensile Strength (MPa) | Elongation (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| DX51D+Z | ≥140 | ≥270 | ≥22 |
| SGCC | ≥205 | ≥270 | ≥18 |
| S350GD+Z | ≥350 | ≥420 | ≥20 |
Galvanized steel sheets cover a wide strength range, from commercial-quality materials for forming to high-strength structural grades for load-bearing use.
Formability is a key requirement for bending, roll forming, and deep drawing operations.
The hardness of galvanized steel is governed by the base steel rather than the zinc coating.
Galvanized steel sheets are generally weldable using standard resistance or arc welding techniques.
In summary, galvanized steel sheets combine predictable mechanical strength with long-term corrosion resistance, making them suitable for both forming-intensive fabrication and structural applications across construction, automotive, and industrial sectors.
Galvanized steel is integral to multiple industries due to its adaptability and longevity:

Its resistance to weathering makes it suitable for both commercial and residential buildings.
For applications requiring enhanced slip resistance, such as walkways, stair treads, and industrial platforms, hot-dip galvanized checkered plates are often selected to combine corrosion protection with improved surface safety.
Galvanized components reduce rust-related repairs and extend vehicle service life.
The conductive and protective properties of zinc coatings enhance the safety and reliability of such components.
Coated steel prevents rust under high-humidity or manure exposure.
| Material | Corrosion Resistance | Cost | Formability | Common Use |
| Galvanized Steel | Moderate to High | Moderate | Good | Construction, fabrication |
| Galvalume Steel | Very High | Moderate | Moderate | Roofing, marine structures |
| Aluminum | Very High | High | Excellent | Transportation, marine |
| Electro-Galvanized | Low to Moderate | Moderate | High | Appliances, electronics |
Each coating system is optimized for specific environments and service conditions.
Galvanized steel sheets may be processed further to improve aesthetic or functional characteristics:
Buyers can request surface customization based on intended application or regulatory compliance (e.g., RoHS).
Reliable suppliers provide thorough testing and quality documentation:
| Test/Parameter | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Coating Thickness Test | Confirms zinc mass uniformity |
| Adhesion Test (peel or bend) | Evaluates bonding between coating and base |
| Salt Spray Test (ASTM B117) | Assesses corrosion resistance |
| Mechanical Properties (UTM) | Confirms tensile and yield performance |
| Dimensional Tolerances | Ensures width, length, flatness accuracy |
Certificates such as Mill Test Reports (MTRs), SGS or BV inspections may be required for customs or third-party verification.
Large volume orders can be shipped via bulk vessel or break bulk, particularly for heavy plates or oversized coils.
| Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Production Capacity | Line width, annual output (important for large orders) |
| Certifications | ISO 9001, CE, SGS, BIS, or UL, depending on region |
| Customization | Coating weight, cut-to-length, packaging type |
| Export Experience | Countries served, documentation support |
| Response Time | Ability to quote quickly and ship fast |

CJM is an experienced exporter of galvanized steel sheet and coil, offering:
CJM maintains long-term partnerships with fabricators, traders, and project contractors across Asia, the Middle East, Africa, Europe and America.
Galvanized steel sheets remain one of the most reliable and economical solutions for corrosion-resistant fabrication. Their versatility, availability in standardized forms and grades, and suitability for a wide array of applications make them indispensable in modern industry.
By understanding coating systems, material standards, mechanical behavior, and supply logistics, international buyers can confidently source galvanized products that meet both technical and commercial expectations.
For technical datasheets, or consultation on galvanized steel solutions, reach out to CJM’s professional export team.
Email: info@cjmstainlesssteel.com
WhatsApp: +86 18191906640
Compare cold rolled vs hot rolled steel for appliances. Learn which steel suits appliance panels, frames & manufacturing needs based on strength and cost.
View detailsExplore 4Cr3Mo3SiV tool steel properties and applications. Find GB 4Cr3Mo3SiV steel plates, suppliers, and manufacturers for hot work and cold work dies.
View detailsDiscover 4140 steel overview: key specifications, broad applications in automotive, machinery, and energy industries and main features for buyers and engineers.
View detailsCompare ASTM A709 steel plate grades 50, 50W, and HPS 70W for bridge construction. Learn strength, weathering performance, and typical applications.
View details
HelloPlease log in